
What is Plastic Injection?
Plastic injection is a manufacturing technology for mass production of identical low-error plastic parts. In plastic injection, the polymer granules are first melted and then pressurized into a mold.
Introduction to Plastic Injection Process:
Plastic injection is a manufacturing technology for mass production of identical low-error plastic parts. In plastic injection, the polymer granules are first melted and then pressurized into a mold. The liquid plastic inside the mold cools and solidifies. Plastic injection materials are thermoplastic polymers that can be stained and filled by other additives.
Almost all of the plastic parts we use everyday are made using plastic injection technology: from auto parts and electronics to kitchen appliances.
Due to the popularity and widespread use of plastic injection, the cost of each piece is very low in high circulations. Plastic injection offers high reproducibility along with high design freedom. The main limitations of plastic injection are economical because, although high-throughput plastic injection production is very cost-effective, relatively high initial capital is needed to start the process. Another limitation of plastic injection is the relatively high time it takes for a piece to be produced.
We first see how plastic injection parts are made and how plastic injection technology works. We also review the general features of this process that influence the design of a piece for plastic injection. We will go into the mechanics of plastic injection technology in more detail, examining the impact of this work on the cost of manufacturing with this technology, and consider its key capabilities and limitations.
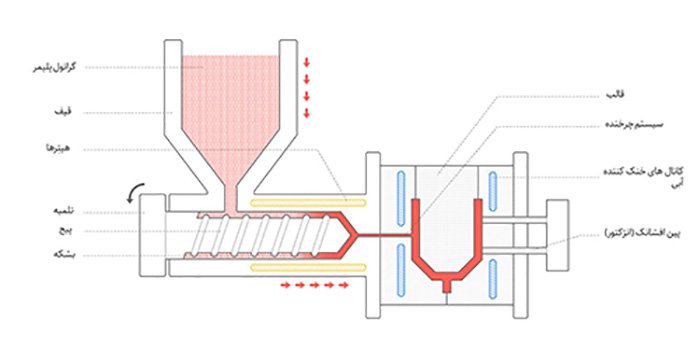
How Does Plastic Injection Work?
Plastic injection workmanship:
- The polymer granules are first dried and placed in a hopper. These granules in the hopper combine with powder and color pigments and other booster additives.
- The granules are fed into the barrel. The granules in the heated barrel are combined with each other and driven by a rotating screw to the mold. The geometry of the bolt and barrel is optimally designed to help raise the pressure to the required extent and to melt the material.
- The pump moves forward and the melted plastic is injected into the mold through the rotary system, filling all the mold space. As the thermoplastic temperature drops, the material becomes solid and forms a mold.
- Finally, the mold is opened and the solid piece is pushed out by the spray pins, then the mold is closed again and the process repeated for the next injection.
Repeating this process can be done very quickly: The plastic injection cycle can usually take from 1 to 2 seconds depending on the size of the piece.
Once the product is ready, the piece is left on the conveyor or in a storage tank. Usually plastic injection molded parts are ready to use as soon as they are manufactured and do not require polishing, polishing or post-processing.
Injection molding
One of the most common and important ways of making plastic parts is the use of injection machines.
Injection molding refers to the process of producing plastic injection products – based on thermoplastic and thermostats – materials after being inserted into the hot cylinder, mixing and then spiraling into the molding quota, where the molded piece becomes cold and hard, Driven. After a piece is designed by an engineer or industrial designer, the mold is tailored to the piece by the molder. Injection molds are generally made of steel or aluminum and precision machined to reflect the design features of the component. Injection molding is used to produce a wide range of products from the smallest objects to the full body of cars.
Injection machines
Plastic injection machines consist of feeding funnel, spiral injection drill and thermal unit. The molds are locked in the clamp plates of the machine and then the plastic is sprayed from the inside of the spray into the mold and injection mold.
Injection machines are divided into different tonnages depending on the amount of force applied to their clamp plates. This force keeps the mold steady and idle during the injection process. The tonnage of the device can range from 1 to 2 tones, though very high tonnages are of relatively less use. The required grip force is determined by the area depicted in the piece. Then, for each square inch of the area depicted, a coefficient of between 2 and 3 tons is multiplied and the required clamping force is obtained. As a general rule, 1 or 2 tons per square inch is a numerically acceptable number for most injectable components. If the plastic used is too dry, we will need more injection pressure to fill the mold, and therefore higher clamping force will be required to hold the mold. Also, the grip force required may be determined by the type of consumable material and the size of the piece: Larger plastic parts will require more grip force.
The production process cycle
The production cycle of the plastic injection process is very short and usually takes about 2 seconds to 5 minutes. This process involves the following steps:
- to close
Before the material is injected into the mold, the first two halves of the mold must be locked together by the clamp unit. Both halves of the mold are attached to the machine, but only one of them can be moved. The clamp unit, relying on hydraulic force, compresses the two halves of the mold and keeps them pressurized during the injection process, with sufficient pressure. The time required to close and compress the two halves of the mold varies depending on the device used: Large machines (those with higher clamping force) will require more time. This time can be estimated with respect to the timing of the device’s idle cycle.
- Injection
Raw plastic materials are usually introduced into the machine in the form of pieces of plastic and driven to the mold by the injection unit. During this process, the material is introduced into the injection mold by application of heat and melting pressure. The accumulation of pressure behind the material will result in a higher density of mold inside the mold. The amount of material needed to fill the mold space is called a shot. Due to the complex and variable flow of materials in the mold, it is generally difficult to calculate and estimate the injection time. However, this time can be evaluated in terms of the amount of shot required, the pressure, and the power of the injection.
- cooling
The molten material inside the mold will gradually lose heat as it contacts the inner surface. At the same time, the material will take shape and shape of the piece in question. However, during this time the phenomenon of fragment shrinkage may also be linked. The accumulation and flow of more material into the mold during the injection phase can reduce the amount of visible shrinkage. The mold remains locked and idle until the end of the cooling period. Also, the cooling time can be estimated taking into account the thermodynamic properties of the plastic as well as the maximum thickness of the piece.
- Exit the piece
After sufficient time, the chilled piece can be removed from the mold by means of an embedded system at the back of the mold. When the mold returns, a special mechanism is applied by pushing the piece out. The need for this pressure is that the piece is absorbed into the core of the mold as it cools down. Spraying auxiliary elements to the interior of the molding quetta is sometimes used to facilitate the removal of the part, sometimes prior to injection. The time required to open the mold as well as the complete ejection of the piece can be estimated from the device’s cycle time. After removing the piece, the mold is locked again and ready for the next shot injection.
Inflatable molding
Inflatable molding is a manufacturing process used in the manufacture of hollow plastic parts such as plastic bottles. Injection molding is done in three ways: extrusion blow molding, injectable blow molding, tensile injection blow molding.
The molding process begins with heating the plastic and creating the initial melt, the melt being a cylinder with a threaded free end that air can pass through, then the melt is put into the mold and the wind blows, the plastic wind pressure Pushes and attaches to the mold wall, after the plastic has cooled and cooled the mold opens and the piece is removed. In the other two ways, the injection mold is created in a special mold. At the blasting stage, the last method, ie, injection molding, kills a heated melt rod while the air is blown.
Types of inflatable molding
- Extrusion wind molding
- Injection air molding
- Injection Molding Injection Traction
Extrusion wind molding
In this method, the plastic is melted and then extruded into the form of a mouthpiece, then the mouthpiece goes into the mold and the wind blows through it, after the mold is cooled and the piece is removed. This process is done in two ways, one continuous and one alternating, in the continuous process the plastic granules are extruded continuously and the initial mounds are produced, then inserted into the mold and the air is pressurized. In the alternate process, the thread is first created at the top of the mouthpiece, followed by the injection of the mouthpiece, and then blown. In continuous molding, the weight of the mouthpiece changes its thickness and makes it difficult to create a uniform thickness. To solve this problem, hydraulic systems quickly remove the mouthpiece to minimize the effect of weight on the wall thickness.
For example, milk bottles, shampoo bottles and sprinklers are produced in this way.
The advantage of this method is its low cost, high production speed and the ability to create complex parts.
The disadvantages of this method are its limited internal components and low rigidity
Injection air molding
This method is used for mass production of interior glass and plastic parts. In this method, the initial incision is made by injection and then the wind is blown in. This method is less used than other wind-forming methods and is more commonly used to produce disposable medicinal containers. In short, the process is divided into 4 parts: injection, blowing, throwing.
In this process, the polymer granules are first melted in the extruder, then injected with a nozzle into a mold and the melt is created, then the melt is removed from the mold and inserted into another mold until the wind blows, after the mold has cooled. And the piece goes out.
